Avoid that toothache by taking extra care
What you need to know:
- Most times it is only pain that will make one visit a dentist
- The prevalence of oral infections in Uganda is generally low among the urban elites
For many of us, it is usually after a painful toothache that will deny us sleep that we decide to visit a dentist.
Because of this, we suffer negative dental conditions that could have been addressed earlier than when it is a little too late.
A common yet avoidable and treatable dental condition is calculus or tartar, also known as dental deposits (calculi).
What it is
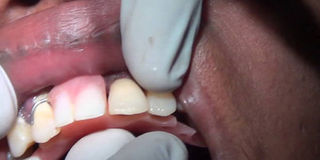
Calculi are heavy stains and deposits on the surface of the teeth, along the gum line.
It is caused by a hardened plaque that attaches on the enamel of the teeth and below the gum.
Every time we eat, there are small food particles that remain on and in our teeth, and when these are not removed (through brushing) they are worked on by the minerals in the saliva, and become plaque.
“This substance is a sticky colourless film of bacteria that constantly forms on teeth and along the gum line,” Benon Muranga, a dentist at Mwatu Dental Clinic, explains.
When the plaque is not removed, it leads to calculi build up, which compromises the health of gums.
This causes cavities and gum disease formed along the gum line and within the narrow furrow between the teeth.
This condition is associated with a number of clinical manifestations including bad breath, receding gums (where the gum continually breaks down and diminishes) and chronically inflamed gums (the gum is reddish, bleeding, swollen)
Causes
“There is a possibility of developing plaque. It is just a matter of continuously cleaning our teeth so that the plaque does not accumulate into calculi,” Muranga says.
External factors that facilitate accumulation of calculus include smoking, diabetes, dehydration, and generally, conditions that do not allow to proper brushing or even brush at all, such as sickness.
Symptoms
Yellow or brown stains on the teeth, are likely to develop into calculi. The colour differ depending on what one eats.
So, the colour may range from green, white or yellowish.
In its late stage, calculus usually develops into a hardened black mass along the gum line.
It starts to creep under the gums and attack the surrounding tissue – causing disease that could lead to loss of teeth.
It is therefore imperative that as soon as one notices those stains they are immediately removed by a dental hygienist.
Consequences
According to Muranga, neglect can lead to tougher consequences like tooth decay loose.
“Calculi above the gum line irritates and damages the gum. Overtime, this can lead to diseases such as gingivitis, where the gum is inflamed, and in its late stage, periodontitis [a condition where the pockets between the gum and teeth are infected by bacteria which slowly, but progressively, damages the soft tissue and the bone that supports the tooth],” he says.
Prevention
To prevent dental calculi, one has to remove its source - dental plaque
But also one should avoid sugary snacks as well as going for regular check ups at least twice a year to keep dental calculi from building up.
Practice excellent oral hygiene (brush at least twice a day and floss at least once a day. If possible, brush after every meal to keep dental plaque and tartar from forming. Ensure proper brushing.
Toothpaste with an additive ingredient of zinc citrate has been shown to significantly reduce plaque.
But also toothpaste with an abrasive is effective in cleaning without damaging the enamel.
Treatment
“Removal of plaque prevents permanent tooth decay. Bigger problems arise if plaque stays on your teeth and hardens into tartar. Once it does so, only a dentist or a dental hygienist can remove it,” Muranga advises.
Through treatment known as dental scaling and root planning, dentists can be able to dislodge dental calculi, even from under the gum.
It is also recommended that, in whatever health condition, people should go for medical checkups.
“We have a high disease rate and it is partly because many people don’t engage in frequent medical checkups,” Muranga explains.
Diseases that would have been diagnosed earlier enough are presented to doctors when it is too late.”
Tit bits
Cause. A number of external factors such smoking, diabetes, dehydration, and sickness can cause calculi, not cleaning your teeth is the lead cause.
Symptoms. Yellow or brown stains on the teeth that are likely to develop into calculi, if left uncleaned.
Prevention. To prevent dental calculi, one has to remove its source; dental plaque. However, it is also important that one takes on regular checkups at least twice a year to keep dental calculi from building up into control.
Treatment. Removal of plaque prevents permanent tooth decay. And this can be done through dental scaling and root planning.




