Lumumba's coffin visits Kisangani, where Congo's first premier found his way

This videograb taken from AFPTV footage, shows the coffin of slain Congolese independence leader Patrice Lumumba being carried by military personnel from an aircraft on arrival at Tshumbe in DRCongo on June 22, 2022. PHOTO/AFP
What you need to know:
- From Kisangani, the coffin will be taken on Sunday to Katanga in the southeast, where a secessionist movement raged after independence and where Lumumba and his aides were tortured to death.
- The burial ceremony in Kinshasa is planned for June 30, which is Independence Day.
After a rest in his native village, the coffin of the former Belgian Congo's first post-independence prime minister Friday pursued its memorial pilgrimage to the northeastern city of Kisangani.
As in Onalua village in the centre of today's Democratic Republic of Congo, where Lumumba was born in 1925, officials, dancers and tam-tams in Kisangani awaited the remains of the independence hero, executed in January 1961, four months after the end of his brief term in office.

Military personnel hold a portrait of slain Congolese independence leader Patrice Lumumba as they ride in a convoy with his coffin after its arrival at Tshumbe in DRCongo on June 22, 2022. PHOTO/AFP
A single tooth is all that remains of the young scholar and nationalist politician whose life and career were cut short in a dark struggle for leadership and control of resources in the central African country.
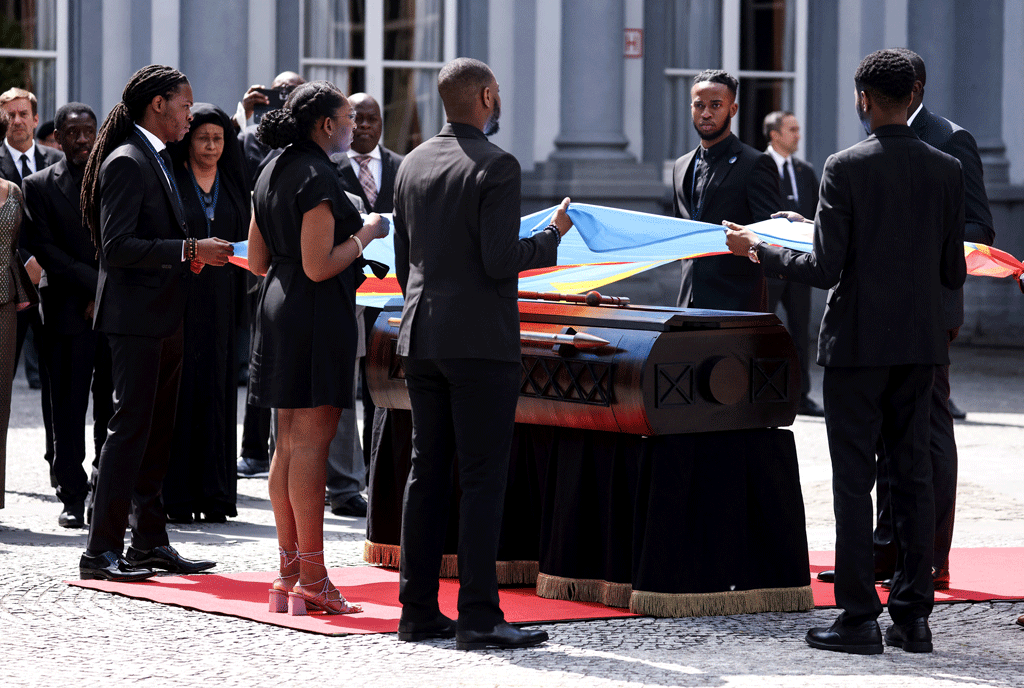
His body was dissolved in acid after he was killed, but a Belgian police officer kept the tooth as a trophy. Belgian authorities in 2016 seized the relic from his daughter.
Belgium finally returned it on Monday to Lumumba's family members during a ceremony in Brussels.
It was then placed inside a coffin for the funeral tour, 61 years late.
'I protect Lumumba's chair'
In a small room inside a brick building known as "1925" in Kisangani, the shelves are stacked with records and works of the colonial administration in Stanleyville, as Kisangani used to be called.
Titles ranged from "Congo Codes and Laws, 1954" and "Legal Review of the Belgian Congo" to "Palm groves in relation to ethnology".

Patrice Lumumba salutes the photographers as he leaves the Idlewild airport on August 2, 1960, to go to his hotel in New York. Leader of the Congolese national movement, he became the first Prime Minister (1960) of the new state Democatic Republic of the Congo, former Belgian Congo, renammed Zaïre in 1971. Arrested in November 1960 and deposed, he was assassinated in January 1961. PHOTO/AFP
Patrice Emery Lumumba worked here as a librarian for the Indigenous Labour Administration. He was also in charge of mail at the Post Office.
Joseph Lifaefi, head of an office that watches over the property, says he has heard talk of "a tourist site, but nothing concrete".
"I protect Lubumba's table and chair, the writings with his signature, his demands," he told AFP, showing the wooden chair and old grey table.
He voiced concern for precious documents, some of which date back to the 19th century, that he said should be digitised.
"This makes me feel ashamed," Lifaefi said. "There should be a museum here."

Three children of Patrice Lumumba, Juliana Lumumba (L), Roland Lumumba (2ndR) and Francois Lumumba (R) pose with King Philippe - Filip of Belgium (2ndL) at the Royal Palace ahead of the official ceremony to hand over a tooth of Democratic Republic of Congo's first Prime Minister and independence hero Patrice Lumumba in Brussels on June 20, 2022. PHOTO/AFP
Lumumba was just 20 when he arrived in Stanleyville, a junior civil servant appointed to handle postal cheques. He went on to become the commercial director of a large brewery.
"My father was the first to welcome him," said Pauline Kimbulu, daughter of Paul Kimbulu, one of the few qualified nurses from colonial days.
"He came to eat here," Kimbulu added in front of a small home with cement walls and a tin roof.
"Let someone restore this house."
'Extreme ambition'
As years passed, Lumumba gained confidence and "strength of conviction" matched with eloquence and easy charm, according to Belgian cultural historian and journalist David Van Reybrouck in his prize-winning work "Congo, the Epic History of a People".
He lived until the late 1950s in Commercial District Five, where little tarmac remains on his street and the electricity supply died two years ago.
He held meetings at the mythical "Circle of State of Mangobo", a hall that is now a ramshackle depot for furniture and coffins for sale.
Leader of a trade union branch, head of a local association of "evolved" minds, author of political analyses and newspaper columns, Lumumba also possessed what Van Reybrouck described as "extreme ambition".
In 1958 he launched a political party, the Congolese National Movement (MNC), which won national elections in May 1960, a month before independence.

Dancers perform next to the coffin of Democratic Republic of Congo's first prime minister and independence hero Patrice Lumumba during a tribute ceremony at The Congolese Embassy before the departure of his last remains to DR Congo in Brussels on June 21, 2022. PHOTO/AFP
Blaise Tresor Badjoko, a neighbour, says that his father came to live in Lumumba's home after his assassination, and died under the same roof. Badjoko believes that Lumumba's remains should rest in Kisangani, rather than in the capital Kinshasa.
From Kisangani, the coffin will be taken on Sunday to Katanga in the southeast, where a secessionist movement raged after independence and where Lumumba and his aides were tortured to death.
The burial ceremony in Kinshasa is planned for June 30, which is Independence Day.